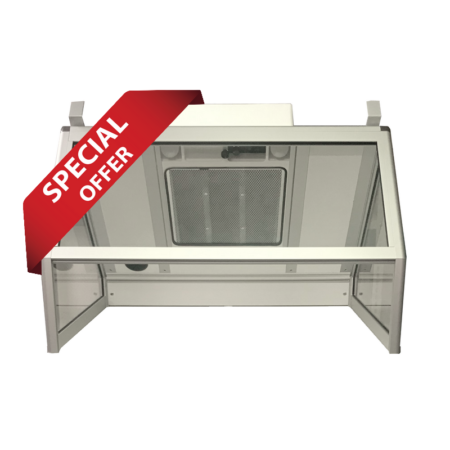
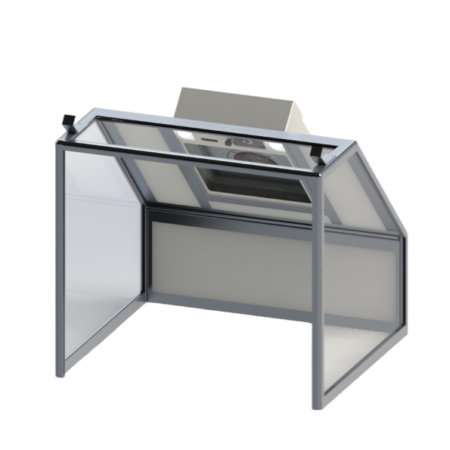
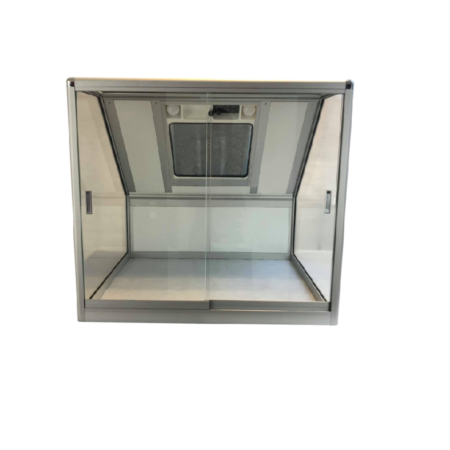
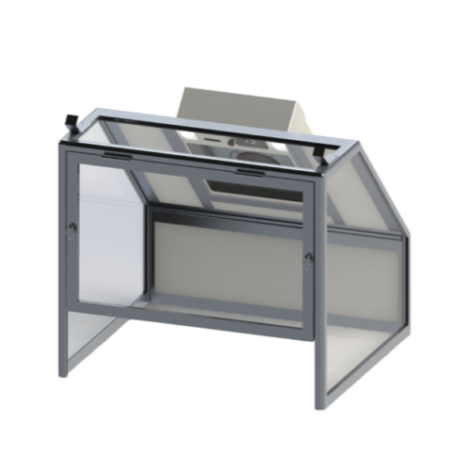
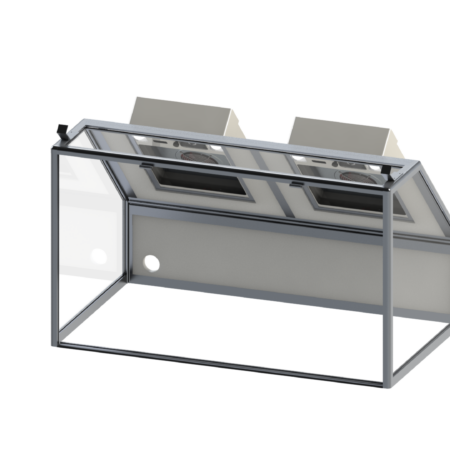
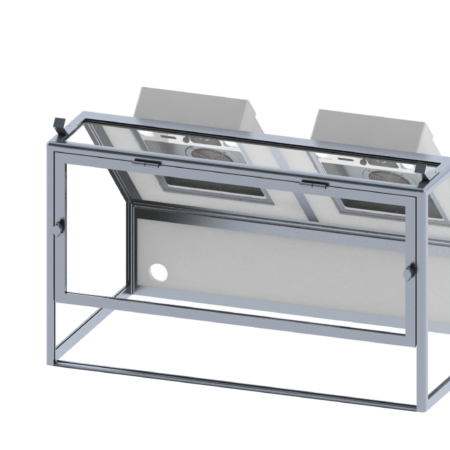
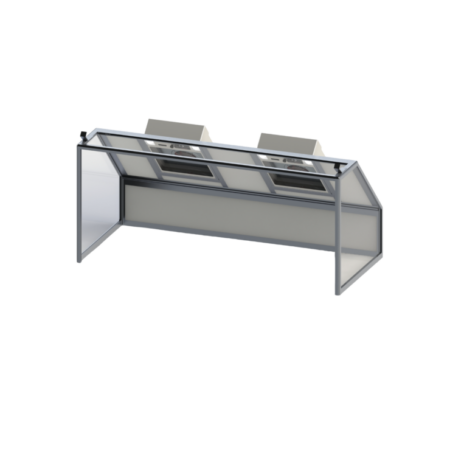
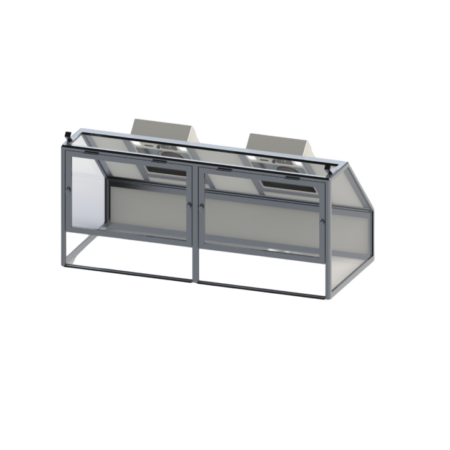
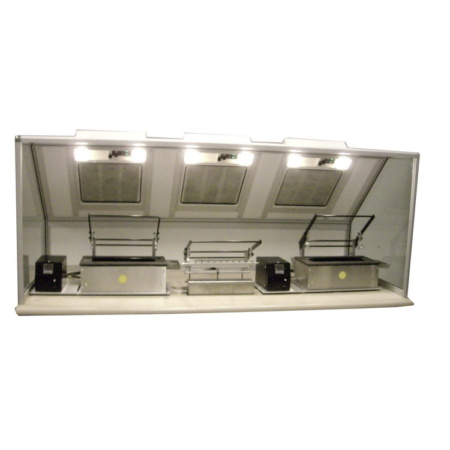
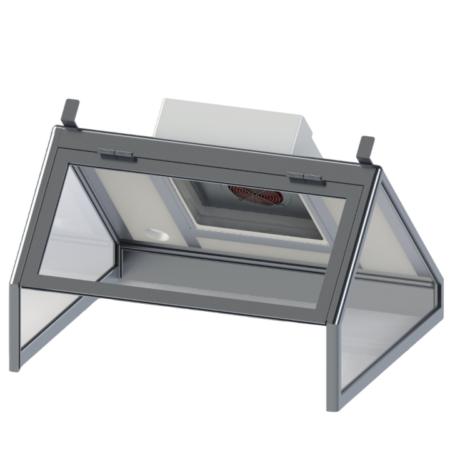
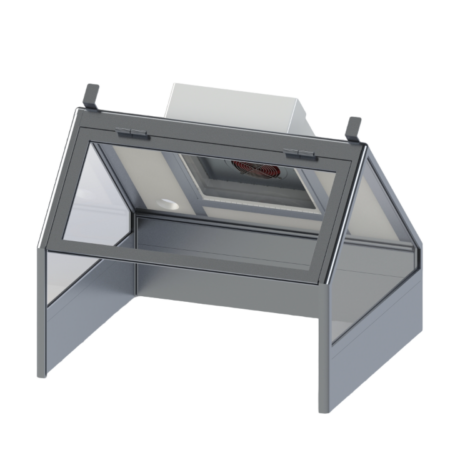
Our cabin hoods are designed for applications requiring space confinement
By reducing the volume to be treated, they make it possible to filter more polluting activities such as: spray applications, handling of chemicals or volatile solvents, varnishing or potting, etc.
Our standard hoods are of two types:
- Pyramids for working above the work surface
- Straight with or without door
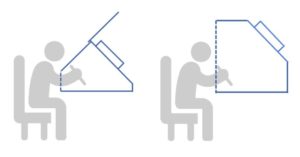
We also manufacture tailor-made cabin hoods of all sizes and shapes.
Do not hesitate to contact us to tell us about your project!
FAQ – Standard cabin fume hoods (air filtration)
What is the purpose of a cabin fume hood?
What are the typical applications?
- Solvent cleaning (acetone, MEK, etc.)
- Varnishing, gluing, potting
- Tinning, brazing / desoldering
- Use of aerosols (spray cans, spray guns)
- Machines generating heavy fumes
- Applications generating very fine particles (< 0.3 µm)
What airflow configurations are possible?
- Recirculating (ductless) mode: the air passes through the filters then is returned to the room.
- Ducted exhaust mode: the air is discharged via a Ø125 mm duct located at the rear of the extraction unit.
Important: recirculating mode must not be used where there is a carcinogenic, mutagenic or reprotoxic (CMR) risk.
What standard models do you offer?
- Pyramidal cabins (e.g. HI7VP, HI7VPR)
- Straight single-operator cabins (HI5VP, HI5VPP, HI5VPC)
- Multi-operator cabins (HI5VP-1200-2GR, HI5VPP-1200-2GR, HI5VP-DOUBLE…)
External widths from 800 mm to 1572 mm depending on the version.
What customisation options are available on standard cabins?
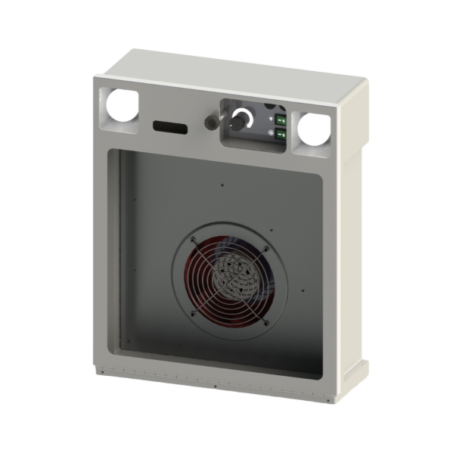
- Reinforced extraction unit up to 600 m³/h (instead of 450 m³/h)
- Motion sensor start/stop
- Retention tray for hazardous products
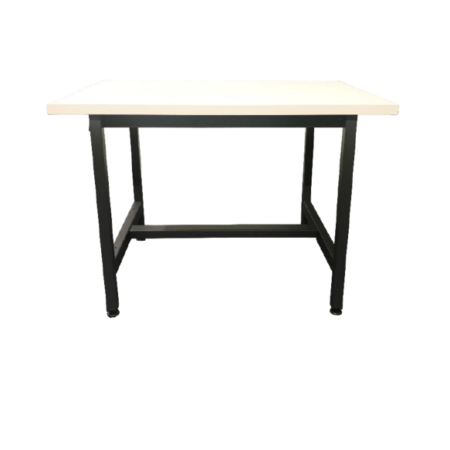
- Workbench / stand
- Riser / height extension (to increase hand-access height)
What filter stack do you recommend?
For workstations combining particles and VOCs, the recommended order is:
- Pre-filter (class M5): protects the downstream filters and extends their service life.
- HEPA filter (H14): captures very fine particles.
- Activated carbon filter: adsorption of solvents and VOCs.
What types of filters do you use?
Summary (in stack order)
| Stage | Reference / Description | Main use | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-filter | PF3 / Protective pre-filter | Upstream protection (prevents clogging of the following stages) | M5 |
| 2. HEPA filter | FHP1 / High-performance filter | Very fine particles (down to 0.1 µm) | H14 |
| 3. Activated carbon | FCP1 / FCP1 min / FCP1 blend / FCP1-FT (acid or base) | Solvents, VOCs, gases (impregnated versions for acids/bases, blend version for formaldehyde, etc.) | — |
For ducted exhaust, use a dust filter (FPP1) upstream of the Ø125 mm duct.
What extraction airflow can I expect?
- Standard: 50 to 450 m³/h (adjustable via speed controller)
- Reinforced option: up to 600 m³/h
- Multi-operator cabins: up to approx. 1200 m³/h (2 extraction units)
How should the hood be maintained?
- Replace filters according to usage and monitor pressure drop.
- Check airflow and speed-controller operation regularly.
- Clean glass surfaces and the work surface.
- Do not use recirculating mode in the presence of carcinogenic, mutagenic or reprotoxic (CMR) risks.
- Display 36 Products per page